News, Blogs & Case Studies
- All
- News
- Blogs
- Case Study
New Geotechnical Engineer bolsters GeoGrow's technical capabilities
We’re pleased to welcome Babikir Hasan to the team as our new Geotechnical Engineer. His arrival adds valuable experience and technical know-how to our growing team.
GeoGrow welcomes new additions for 2025
As we enter 2025, we are delighted to have made some new additions to make strides in the civil engineering industry.
Steady Growth : Our new Deputy MD Natalie Harris
GeoGrow is proud to announce the promotion of Natalie Harris to the position of Deputy Managing Director.
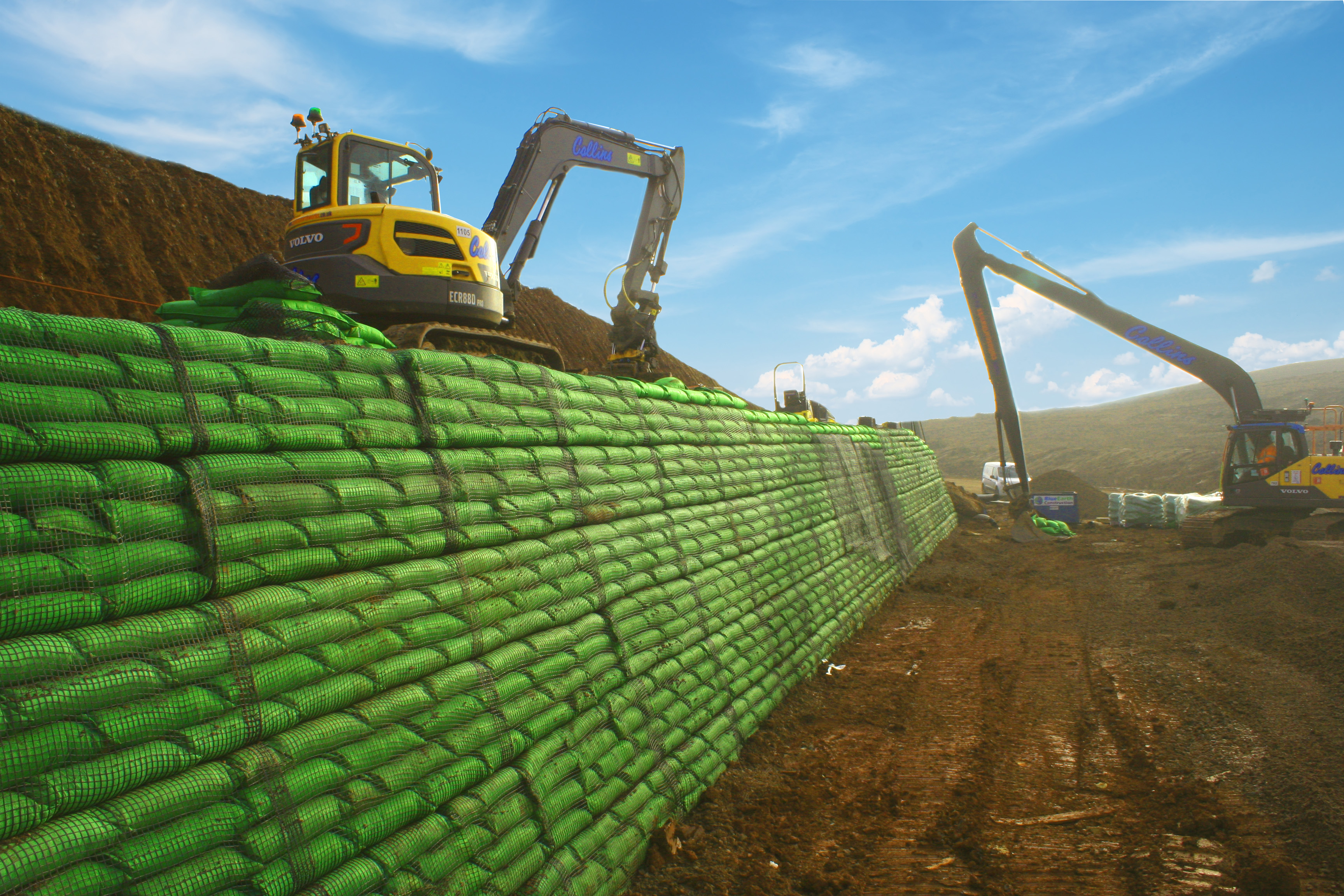
The role of vegetated retaining walls in sustainable construction
We take a look at how retaining walls can maximise sustainability in your next project
Hydroseeding: A solution for erosion control & landscaping
This cost-effective and efficient technique involves spraying a slurry of seed, mulch, fertiliser, and water onto the soil, promoting rapid vegetation growth and reducing erosion.
Manufactured in the UK
We are committed to supporting British manufacturing, with our products designed and produced right here in the UK.
Working together to protect the future of the UK's wildlife
We are entirely committed to supporting biodiversity.
A practical hydroseeding guide for contractors and site managers
Hydroseeding is a fast, solution for establishing vegetation over varying areas, but the real success of a hydroseeding project depends on the aftercare.
Comprehensive design capabilities tailored to your project
We understand that great outcomes start with great design. That’s why we offer a full spectrum of design services, developed to guide our clients from initial ideas through to detailed, build-ready solutions.
Rootlok secures Blythe Valley Business Park
We worked closely with the land agent managing the business park to design and implement an environmentally friendly solution.
Hydroseeding success at Halesfield
Turning this bleak, unappealing landscape into a vibrant, environmentally friendly green space. Learn more about our successes at this site in Halesfield
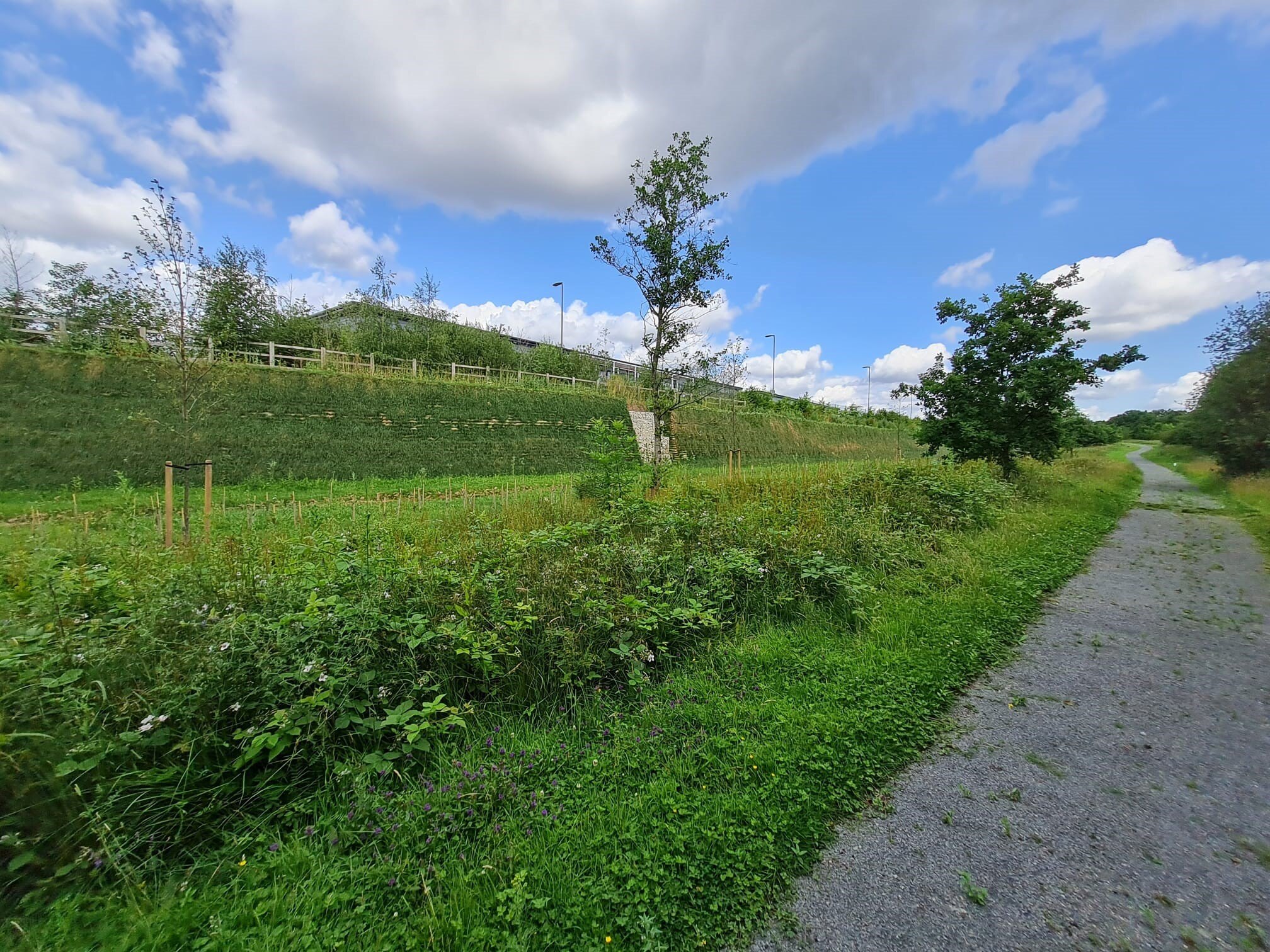
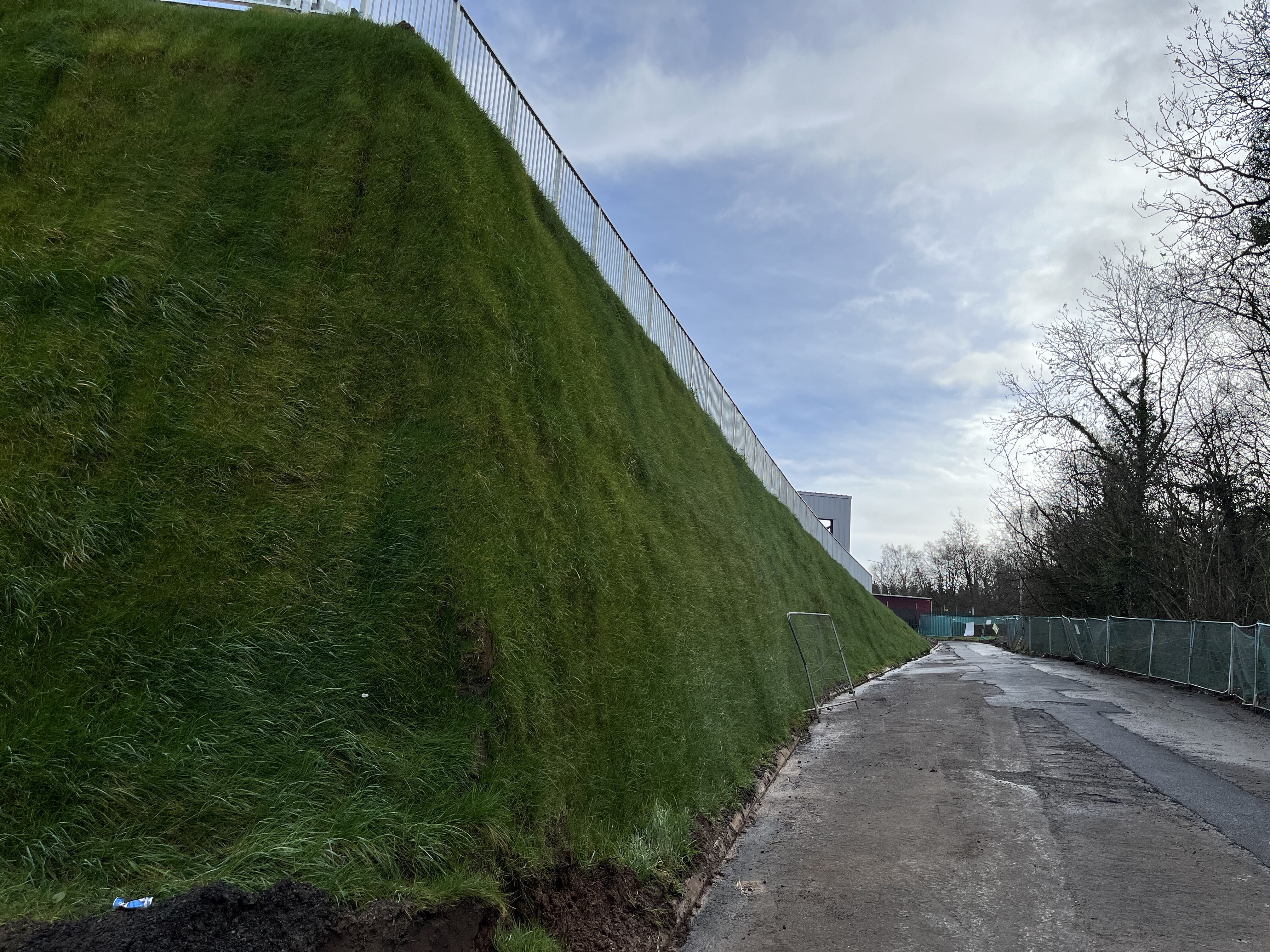
Sustainable solution at Linmere
We were asked to create a retaining wall fixed to an existing sheet pile wall. The client needed a sustainable solution that suited the surrounding landscape.
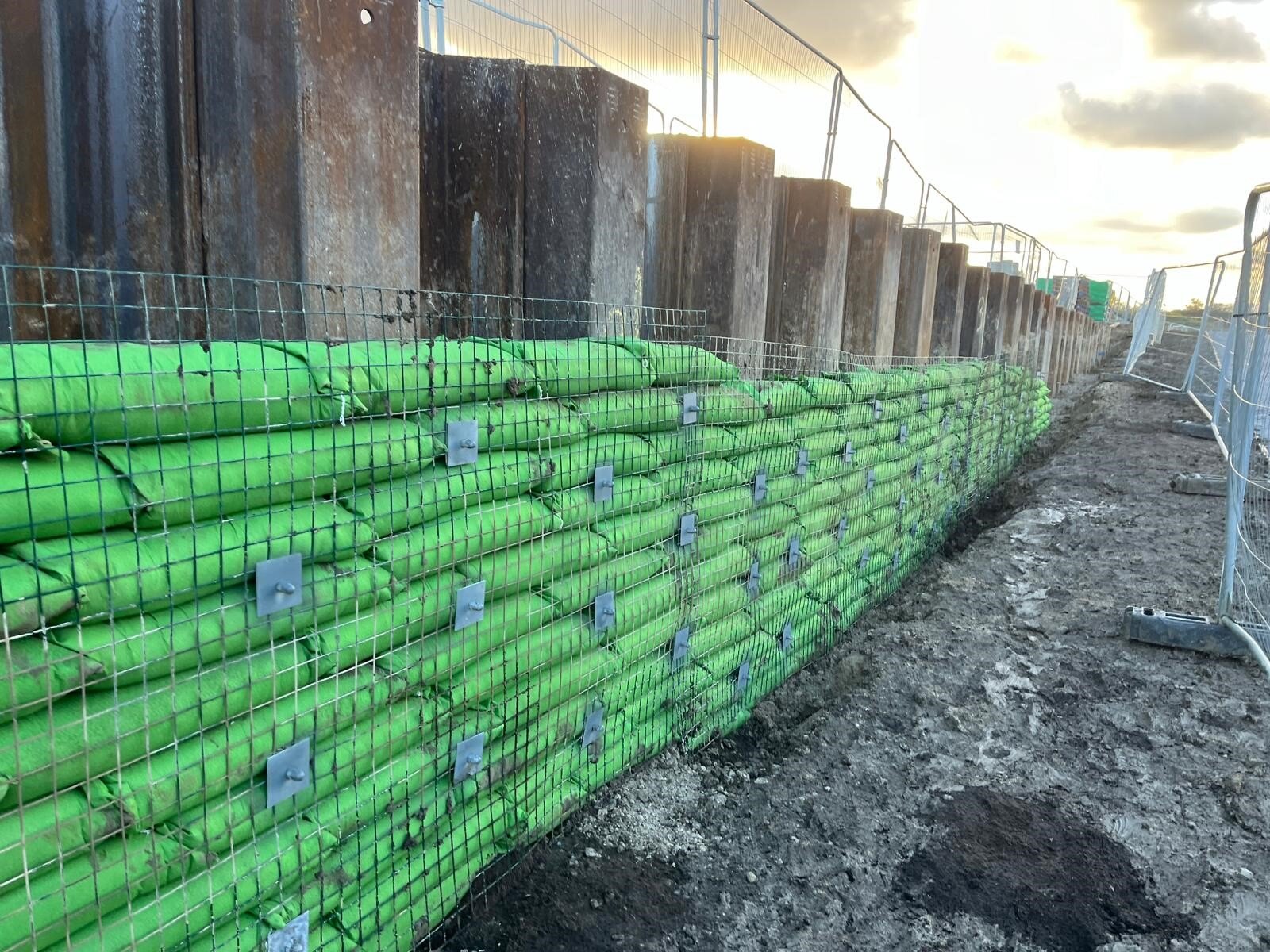
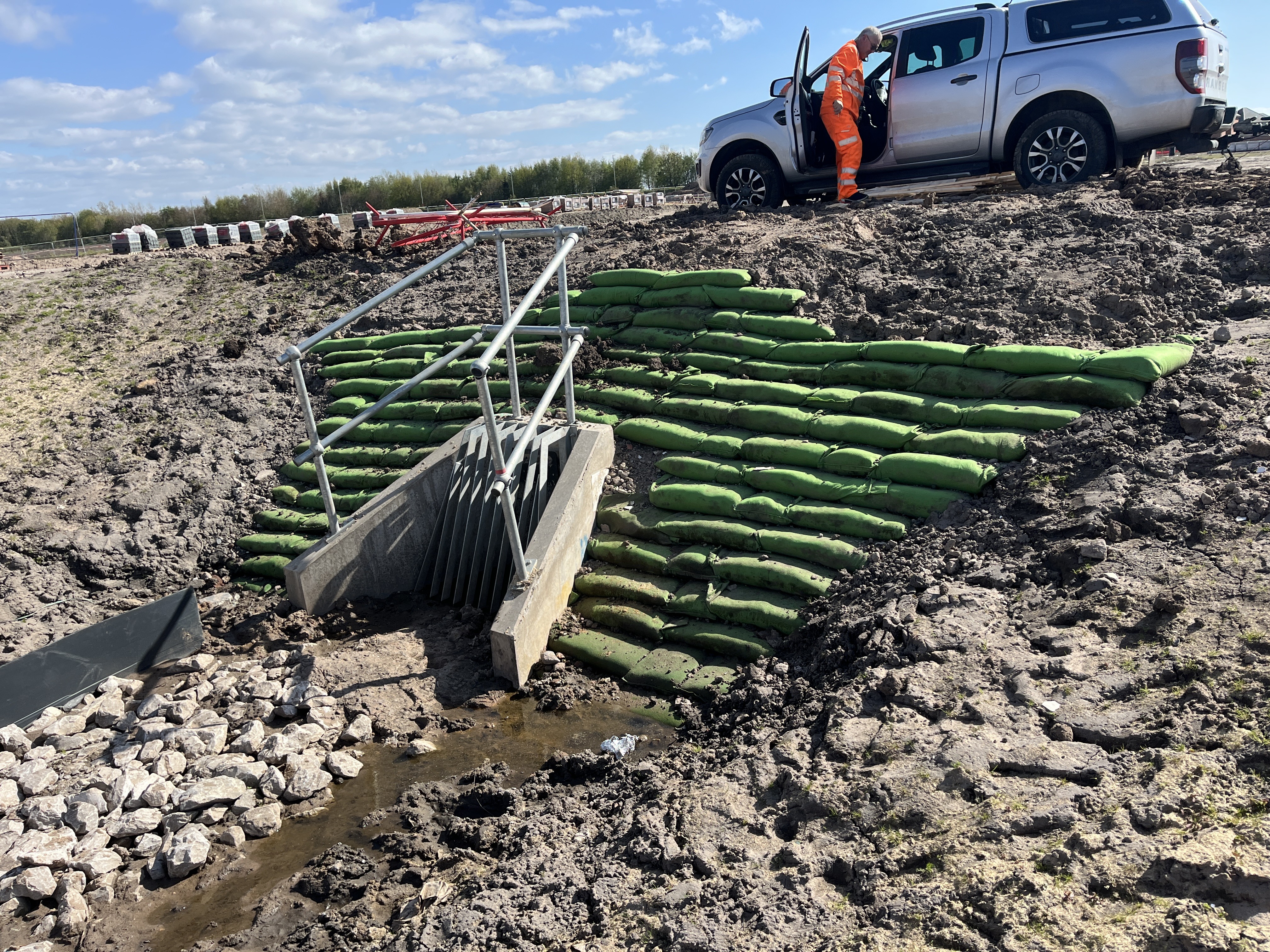
Headwall scour protection and hydroseeding
We implemented Rootlok as scour protection around a headwall and hydroseeded swales as part of a development project in Liverpool.
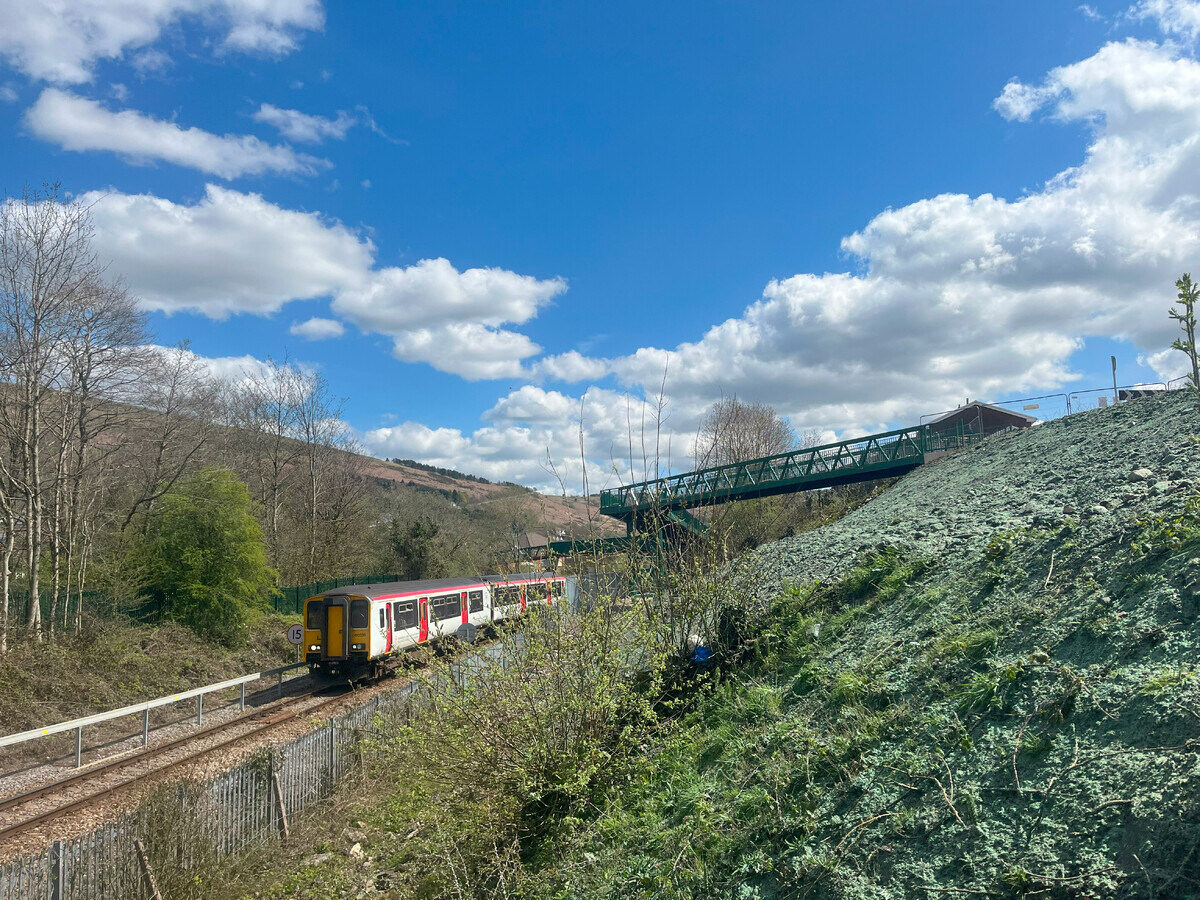
Transforming Pentre rail embankment
Railway infrastructure projects often present unique challenges and at a site in Pentre, we were asked to hydroseed a newly profiled rail embankment.
Transforming a challenging basin into a thriving green space
At the forefront of a new housing development in Lawley Village, Telford, we were tasked with hydroseeding an attenuation basin to create a sustainable, vegetated landscape.